中國歷史
中國歷史
History of China: An Overview of Ancient Foundations, Dynastic Changes, Modern Transformation, and Global Influence
The Ancient Foundations of China
Origins of Chinese Civilization:
The history of China dates back thousands of years, with its roots in one of the world’s earliest civilizations along the Yellow River (Huang He). The Xia Dynasty (2070–1600 BCE), regarded as the first dynasty in Chinese history, laid the foundation for later societal structures. While its historical existence has been debated, it is often seen as the birthplace of Chinese governance and culture. Following the Xia, the Shang Dynasty (1600–1046 BCE) further developed China’s political, social, and technological systems, including the use of bronze for tools and ceremonial objects. It was during this period that the earliest Chinese writing system emerged, carved into oracle bones for divination.
Philosophical and Cultural Beginnings:
Ancient China’s philosophical and cultural foundations were shaped by the Confucian, Daoist, 和 Legalist schools of thought. Confucianism, founded by Confucius (551–479 BCE), emphasized ethics, filial piety, and proper social relationships, forming the backbone of Chinese moral philosophy. Daoism, founded by Laozi (6th century BCE), emphasized harmony with nature and the pursuit of simplicity, influencing Chinese thought and arts for centuries. Legalism, on the other hand, focused on strict laws and harsh punishments to maintain order and stability, which were instrumental during certain dynasties like the Qin Dynasty.
Major Contributions:
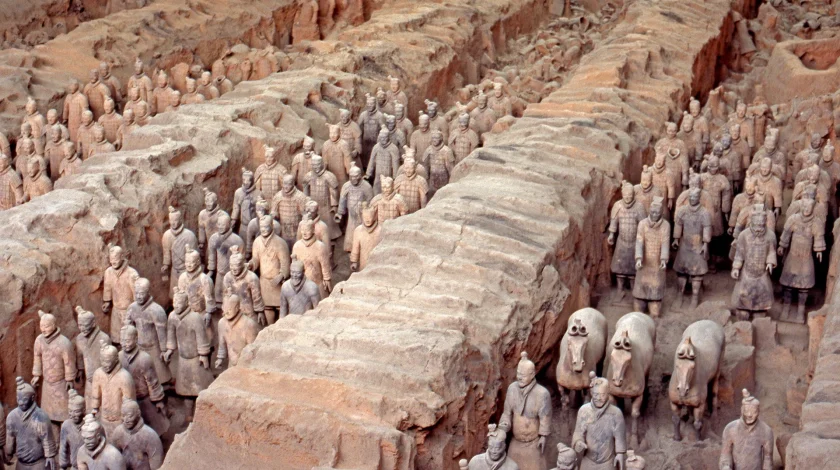
China made immense contributions to human civilization, especially in the fields of technology, writing, 和 philosophy. One of the most significant inventions was the creation of paper during the Han Dynasty (206 BCE – 220 CE), revolutionizing communication. The 中國長城, initially constructed during the Qin Dynasty (221–206 BCE), served as a defense mechanism against northern invasions. Additionally, the development of the Chinese written language, which is still used in modern times, allowed the transmission of Chinese culture and ideas across generations.

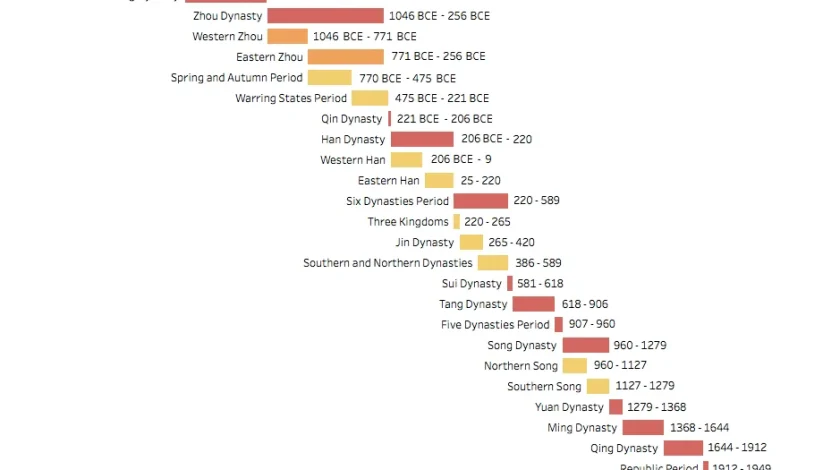
The Rise and Fall of Dynasties
Imperial China and the Dynastic Cycle:
The history of China is characterized by a recurring pattern of dynasties rising and falling, known as the Dynastic Cycle. A new dynasty would rise to power, often through military conquest or the overthrow of a corrupt regime. It would bring peace, stability, and prosperity. Over time, however, the dynasty would become corrupt, inefficient, or weakened by rebellion, leading to its downfall and the rise of a new dynasty.
Key Dynasties and Figures:
Several dynasties played pivotal roles in shaping China’s imperial structure and cultural identity.
- 這 Qin Dynasty (221–206 BCE), though short-lived, was significant for unifying China under Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor, who standardized currency, measurements, and even the writing system.
- 這 Han Dynasty (206 BCE – 220 CE) is often considered a golden age for China, laying the foundations for much of its later cultural and administrative systems. It was during this period that 絲路 trade flourished, connecting China with Central Asia and the Roman Empire.
- 這 Tang Dynasty (618–907 CE) saw a flourishing of art, literature, and trade. Li Bai 和 Du Fu, two of China’s greatest poets, emerged during this period, and Empress Wu Zetian became the only female emperor in Chinese history.
- 這 Ming Dynasty (1368–1644) saw the construction of the 故宮 and the development of Chinese culture and global trade, particularly through the voyages of Zheng He.
- 這 Qing Dynasty (1644–1912) was China’s last imperial dynasty, which initially brought stability but eventually faced internal revolts and foreign incursions that led to its collapse in the early 20th century.
Cultural Flourishing and Decline:
China’s imperial history is marked by periods of prosperity, often defined by technological advancements, cultural production, and the flourishing of the arts. However, as dynasties grew older, corruption and inefficiency often led to their decline. The Taiping Rebellion (1850–1864) and the Opium Wars (1839–1842, 1856–1860) severely weakened the Qing Dynasty and left China vulnerable to foreign influence and control.

Modern China: From the Opium Wars to the People’s Republic
The Opium Wars and the Fall of the Qing Dynasty:
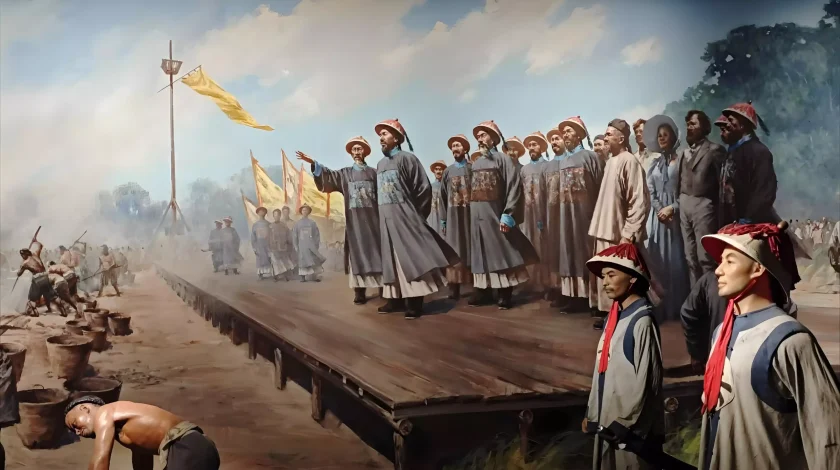
In the 19th century, China faced significant challenges from Western powers. The Opium Wars, caused by Britain’s trade of opium to China, led to humiliating defeats for China and the signing of unequal treaties. These treaties resulted in China losing control of territories such as 香港 and opening up various ports to foreign trade. The decline of the Qing Dynasty accelerated, leading to social unrest and rebellion.
The Republic of China:
在 1911, following the Xinhai Revolution, the Qing Dynasty collapsed, and the Republic of China was established under the leadership of Sun Yat-sen. The Republic faced instability due to warlordism and political fragmentation, but it marked a shift toward modernization and the end of over 2,000 years of imperial rule. Sun Yat-sen’s vision of a democratic republic was challenged by both internal strife and external pressures.
The Chinese Civil War and Communist Revolution:
The Chinese Civil War (1927–1949) was a struggle between the Nationalist Party (Kuomintang), led by Chiang Kai-shek,以及 Communist Party of China (CPC), led by Mao Zedong. After years of conflict, the Communists emerged victorious, establishing the People’s Republic of China (PRC) on October 1, 1949. The victory of the CPC marked the beginning of China’s socialist era under Mao Zedong, who sought to transform China into a communist state through campaigns like the Great Leap Forward 和 Cultural Revolution, both of which had profound social, political, and economic effects.


China’s Contemporary History and Global Role
Economic Reforms and Opening Up:
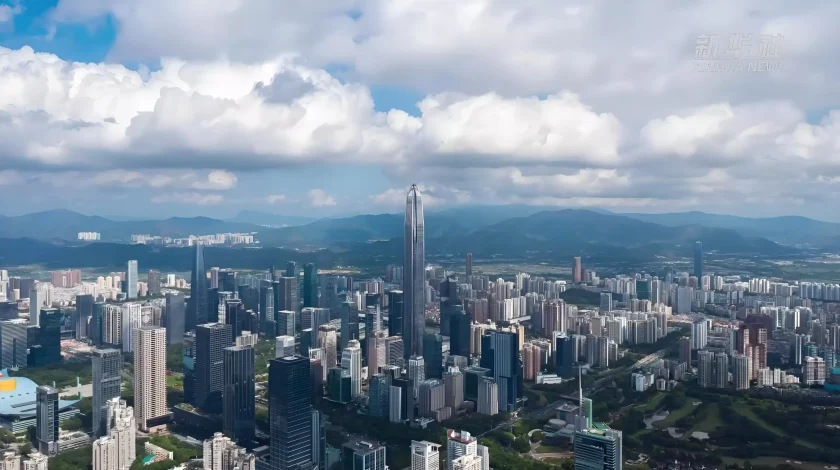
After Mao’s death in 1976, China underwent significant economic reforms under Deng Xiaoping, who introduced market-oriented policies and opened China to foreign trade and investment. The 1978 Reform and Opening-Up policy propelled China’s rapid economic growth, transforming it from a closed, agrarian society to the world’s second-largest economy. The Special Economic Zones (SEZs), such as those in 深圳, allowed China to become a major global manufacturing hub.
China on the World Stage:
In the 21st century, China’s influence on the global stage has grown immensely, with China becoming a major player in global politics, trade, and technology. As a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, China has shaped global diplomacy. Economically, it has become a driving force in global markets, exporting goods worldwide and investing heavily in international infrastructure projects, particularly through the Belt and Road Initiative.
Challenges and Future:
Despite its economic success, China faces several challenges, including environmental issues, income inequality, and political tensions, particularly with Taiwan and other countries in the region. In the 21st century, China’s government under Xi Jinping has focused on maintaining political control while navigating the complexities of global influence. The future of China will likely see continued economic growth, greater technological advancements, and ongoing debates about its role in global governance.

The history of China is a vast and complex story of cultural achievements, dynastic cycles, revolutionary change, and modernization. From its ancient foundations along the Yellow River to its transformation into a global superpower in the modern era, China’s history offers profound insights into its rich cultural heritage, political struggles, and ambitions for the future. Understanding China’s past is crucial to understanding its present and its potential role in shaping the world’s future.
想要更個人化的最佳中國之旅嗎?
與我們聯繫,預訂私人或客製化旅遊,體驗獨特的中國風格。
探索我們最受歡迎的一些旅行行程
旅行回憶
影片推薦
2000 Years of Chinese History! Mandate of Heaven and Confucius
All China's dynasties explained in 7 minutes (5,000 years of Chinese history)
評價








冬季之旅
我們參加了中國冬季旅遊團去哈爾濱參加冰雪節。太壯觀了!雪雕令人嘆為觀止,我們的導遊湯姆確保我們保持溫暖和舒適。火鍋晚餐為我們寒冷的一天畫上了完美的句點。強烈推薦給冬季愛好者!
索菲亞
桂林自然之旅
我們在桂林和陽朔的自然之旅美不勝收。漓江遊船和龍脊梯田健行是亮點。我們的導遊 Leo 了解每一個隱藏的觀點和當地的故事。美麗的風景和熱情的款待使這次旅行令人難忘。
伊莎貝拉

冬季之旅
我們參加了中國冬季旅遊團去哈爾濱參加冰雪節。太壯觀了!雪雕令人嘆為觀止,我們的導遊湯姆確保我們保持溫暖和舒適。火鍋晚餐為我們寒冷的一天畫上了完美的句點。強烈推薦給冬季愛好者!
索菲亞

桂林自然之旅
我們在桂林和陽朔的自然之旅美不勝收。漓江遊船和龍脊梯田健行是亮點。我們的導遊 Leo 了解每一個隱藏的觀點和當地的故事。美麗的風景和熱情的款待使這次旅行令人難忘。





















